
Most machines aren't exploited due to missing patches (although this is the second biggest cause), unpatched zero days (almost never a factor), drive-by downloads, or misconfigurations.
#APPLOCKER SERVICE START UPDATE#
#APPLOCKER SERVICE START FULL#
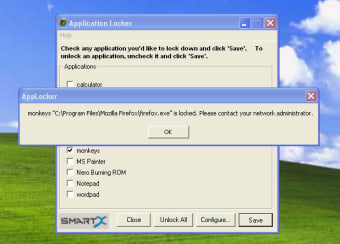
You should always specify the full path to a file or folder when creating path rules so that the rule will be properly enforced. AppLocker does not enforce rules that specify paths with short names.AppLocker uses its own path variables for directories in Windows.The Path condition identifies an application by its location in the file system of the computer or on the network.You can make the rule more generic by moving the slider down or by using a wildcard character (*) in the product, file name, or version number fields. When you select a reference file for a publisher condition, the wizard creates a rule that specifies the publisher, product, file name, and version number.Publisher conditions can be created to allow applications to continue to function even if the location of the application changes or if the application is updated.

#APPLOCKER SERVICE START SOFTWARE#
The publisher may be a software development company, such as Microsoft, or the information technology department of your organization. The extended attributes, which are obtained from the binary resource, contain the name of the product that the application is part of and the version number of the application. The digital signature contains information about the company that created the application (the publisher).

The four rule collections are executable files, scripts, Windows Installer files and Packaged app. The AppLocker GPO setting can be found under Computer Configuration – Policies – Windows Settings – Security Settings – Application Control Policies – AppLockerĪppLocker is organized into four areas called rule collections. AppLocker is configured via GPO by creating various rules to either allow or deny applications.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
